Original Article
Volume: 40 | Issue: 4 | Published: Dec 25, 2024 | Pages: 176 - 180 | DOI: 10.24911/BioMedica/5-1661
Identification of asymptomatic carotid plaques in high-risk middle-aged adults at a tertiary care center in Lahore
Authors: Madiha Naseer , Mahwish Farzana , Zeeshan Ghous , Amna Nasir , Saulat Sarfraz , Waqar Ahmed
Article Info
Authors
Madiha Naseer
Department of Radiology, Shaikh Zayed Hospital, Federal Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lahore, Pakistan
Mahwish Farzana
Department of Radiology, Farooq Hospital, Defense Branch, Lahore, Pakistan
Zeeshan Ghous
Department of Cardiology, Punjab Institute of Cardiology, Lahore, Pakistan
Amna Nasir
Department of Cardiology, Shaikh Zayed Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Saulat Sarfraz
Department of Radiology, Shaikh Zayed Hospital, Federal Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lahore, Pakistan
Waqar Ahmed
Consultant Radiologist, Self-employed, Sargodha, Pakistan
Publication History
Received: October 14, 2024
Accepted: December 15, 2024
Published: December 25, 2024
Abstract
Background and Objective:
There are no comprehensive regional data for Pakistan regarding the frequency of carotid plaques and associated risk factors. Early detection of atherosclerotic plaques by noninvasive screening methods can help reduce the disease burden. As asymptomatic plaques are also one of the major causes of stroke in middle-aged individuals, the present study aimed to identify the frequency and clinical presentation of asymptomatic carotid plaques in high-risk middle-aged patients in local population.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study was conducted at the Department of Radiology, Shaikh Zayed Hospital Lahore, Pakistan. A total of 366 subjects aged 45-81 years old were screened for any atherosclerotic plaques at the bilateral extra cranial carotid artery tree by consultant radiologists through Doppler Ultrasound (DUS). Multi variable logistic regression was applied to determine the variables having an independent association with the development of carotid plaques.
Results:
Carotid artery plaques were diagnosed in 156 (42.62%) patients. Age, sex, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes mellitus showed an independent association with carotid plaques (p-value < 0.001). Present history of smoking was not associated with carotid plaques (P-value > 0.005).
Conclusion:
The diagnostic accuracy of DUS is high for the detection of sub-clinical and clinical carotid plaques. The identification of asymptomatic carotid plaques in high-risk individuals with diabetes and hypertension can save much from debilitating cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Carotid artery plaques, Doppler Ultrasound, Diabetes, Hypertension
Biomedica - Official Journal of University of Health Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
Volume 40(4):176-180
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Identification of asymptomatic carotid plaques in high-risk middle-aged adults at a tertiary care center in Lahore
Madiha Naseer1*, Mahwish Farzana2, Zeeshan Ghous3, Amna Nasir4, Saulat Sarfraz5, Waqar Ahmed6
Received: 14 October 2024 Revised date: 25 November 2024 Accepted: 15 December 2024
Correspondence to: Dr. Madiha Naseer
*Department of Radiology, Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Federal Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lahore, Pakistan.
Email: madihajoiya@gmail.com
Full list of author information is available at the end of the article.
ABSTRACT
Background and Objective:
There is no comprehensive regional data for Pakistan regarding the frequency of carotid plaques and associated risk factors. Early detection of atherosclerotic plaques by noninvasive screening methods can help reduce the disease burden. As asymptomatic plaques are also one of the major causes of stroke in middle-aged individuals, the present study aimed to identify the frequency and clinical presentation of asymptomatic carotid plaques in high-risk middle-aged patients in the local population.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study was conducted at the Department of Radiology, Shaikh Zayed Hospital Lahore, Pakistan. A total of 366 subjects aged 45-81 years old were screened for any atherosclerotic plaques at the bilateral extracranial carotid artery tree by consultant radiologists through Doppler ultrasound (DUS). Multi variable logistic regression was applied to determine the variables having an independent association with the development of carotid plaques.
Results:
Carotid artery plaques were diagnosed in 156 (42.62%) patients. Age, sex, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes mellitus showed an independent association with carotid plaques (p-value < 0.001). The present history of smoking was not associated with carotid plaques (p-value > 0.005).
Conclusion:
The diagnostic accuracy of DUS is high for the detection of sub-clinical and clinical carotid plaques. Early identification of asymptomatic carotid plaques in high-risk individuals with diabetes and hypertension can save from debilitating cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords:Carotid artery plaques, Doppler ultrasound, diabetes, hypertension, asymptomatic.
Introduction
Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of coronary artery disease (CAD) and stroke. There are several imaging modalities, such as computerized tomography, magnetic resonance angiography, and ultrasonography to diagnose atherosclerotic carotid plaques (CP). It is recommended to use noncontact standard economical imaging tools in all patients with suspicion of CP.1 Radiological assessment based on imaging of carotid vessels is more objective and reliable.2Duplex Doppler ultrasound (DUS) is the most widely used modality for the diagnosis of CP, with excellent accuracy comparable to that of angiography due to the lack of contrast and radiation. 3 DUS assesses different blood flow velocity (BFV) parameters such as end-diastolic velocity, peak systolic velocity (PSV), and PSV ratio. BFV is the basis for the diagnosis of extracranial carotid artery stenosis. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) evaluation by carotid B-US is an alternative surrogate technique to detect subtle atherosclerosis.3 Assessment of plaque quantity or plaque area is a more influential measurement than CIMT because it predicts any preemptive clinical occasion. DUS is a useful approach for the screening and diagnosis of CP, as it is a cost-effective and convenient method.
It has been estimated that 8%-15% of total stroke cases are due to complete and incomplete stenosis of the carotid arteries.4 CP undergoes various changes, such as ulceration, calcification, thrombosis, and restenosis.5,6 The subjective assessment of CP by DUS can be made by its echogenicity. Homogenous CP endures more ischemic events than heterogeneous plaques. Heterogeneous CP can easily ulcerate, rupture, and embolize at stress points such as carotid bifurcation. In ruptured plaques, the atheroma attracts platelet aggregation, resulting in the occlusion of small vessels.7-9 Various modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors are associated with myocardial ischemia and stroke. Age, sex, and race are nonmodifiable risk factors. Other potentially modifiable risk factors include diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.10Type II diabetic patients should be routinely evaluated for CAD with abnormal lipid profiles, especially triglycerides and LDL levels. There is a strong positive association between low HDL and hypercholesterolemia with carotid plaques (CPs). 11-14
The major objective of this study is to determine the frequency of carotid plaque thickness in middle age to older patients using Doppler ultrasonography (USG) and to identify the risk factors of carotid plaque thickness. Detailed clinicopathological associations between CP and risk factors in general masses in Pakistan are rarely reported. Hence, we report the identification of CP in asymptomatic individuals and its relationship with various modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors from an urban tertiary care center in Lahore, Pakistan.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Board of Sheikh Zayed Hospital Lahore, Pakistan, and carried out at the Department of Radiology of the same hospital from January 2020 to November 2020. A total of 366 patients were included by nonprobability convenient sampling after informed consent. Patients having age 45-64 years were labelled as middle age and those ≥ 65 years were labelled as elderly were included in our study. Patients with a previous history of stroke, Patients with a past or current history of restenosis, carotid artery endarterectomy, carotid stenting, stroke, and/or myocardial infarction were excluded.
Patients were further subdivided into two groups based on the presence and absence of CP which was defined as a focal lesion into the lumen of any carotid artery having a size of 0.5 mm or covering 50% of the area of the lumen. The following baseline characteristics were recorded: age, sex, diabetes mellitus, blood pressure, serum lipid levels, current smoking habits, and body mass index.
The presence of a focal lesion into the lumen of any carotid artery having size 0.5 mm or covering 50% of the area of lumen was labeled as CP.15 Carotid plaques were measured by Doppler ultrasonography using a GE Voluson Expert 730 machine and probe ranging from 6 to 12 MHz linear array transducer and 36 Hz frequency was adjusted for carotids. A single consultant radiologist with at least 15 years of experience, was assigned to screening of both extracranial carotid artery trees with a special focus on the common carotid artery, bifurcation of the common carotid artery, and internal and external carotid arteries as these are the common sites where plaques are found (Figure 1).
Statistical analysis
The data are expressed as the mean ± SD or frequencies (percentage groups with CP and without CP were compared using a t-test for continuous variables and a chi-square test for categorical variables). Multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to determine the variables, i.e., sex, age, obesity, diabetes, smoking, hypertension, and dyslipidemia that were independently associated with carotid plaques A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
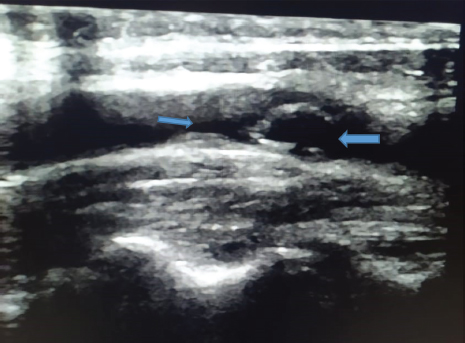
Figure 1. Sonographic image of the artery demonstrating a heterogeneous, lipid-rich, and calcified plaque at the carotid bulb, causing significant luminal stenosis (>70%) (blue arrows).
Table 1. Multivariate analysis showing the association of modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors with carotid plaques.
| Variable | Carotid plaques | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes n (%) |
No n (%) |
|||
| Age | ||||
| ≤64 years | 81 (51.9%) | 147 (70.0%) | 0.46 (0.30-0.71) | <0.0001 |
| ≥65 years | 75 (48.1%) | 63 (30.0%) | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Female (%) | 42 (32.7%) | 106 (50.5%) | 0.36 (0.23-0.56) | <0.0001 |
| Male (%) | 105 (67.3%) | 104 (49.5%) | ||
| Obesity | ||||
| Yes | 44 (28.2%) | 63 (30.0%) | 0.91 (0.58-1.44) | 0.71 |
| No | 112 (71.8%) | 147 (70.0%) | ||
| Hypertension | ||||
| Yes (%) | 91 (58.3%) | 85 (40.5%) | 2.06 (1.35-3.13) | 0.001 |
| No (%) | 65 (41.7%) | 125 (59.5%) | ||
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes (%) | 64 (41.0%) | 67 (31.9%) | 1.48 (0.96-2.28) | 0.07 |
| No (%) | 92 (59.0%) | 143 (68.1%) | ||
| Diabetes | ||||
| Yes (%) | 72 (46.2%) | 73 (34.8%) | 1.60 (1.05-2.46) | 0.02 |
| No (%) | 84 (53.8%) | 137 (65.2%) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | ||||
| Yes (%) | 116 (74.4%) | 123 (58.6%) | 2.05 (1.30-3.22) | 0.002 |
| No (%) | 40 (25.6%) | 87 (41.4%) | ||
Table 2. Location and consistency of carotid plaques on DUS w.r.t gender and associated risk factors.
| Right carotid artery | Left carotid artery | Bilateral involvement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location of plaques | |||
| Common carotid artery | 31 | 35 | 22 |
| Carotid bulb | 14 | 19 | 14 |
| Internal carotid artery | 5 | 10 | 6 |
| Consistency of plaques | |||
| Homogenous | 24 | 42 | 22 |
| Heterogeneous | 26 | 22 | 20 |
| Gender | |||
| Males | 38 | 45 | 31 |
| Females | 12 | 19 | 11 |
| Risk factors | |||
| Diabetes | 20 | 27 | 25 |
| Hypertension | 29 | 41 | 21 |
| Dyslipidemia | 31 | 52 | 33 |
| Present history of smoking | 24 | 20 | 20 |
Results
Carotid artery plaques were diagnosed in 156 (42.62%) patients. The mean age of the patients was 61 ± 12 years, and 46% of the participants were males (Table 1) The multivariate logistic regression analysis of independent predictors, i.e., age, sex, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and current smoking reveals the overall frequency of hypertension (58.3% vs. 40.5%, p > 0.0001), diabetes mellitus (46.2% vs. 34.8%, p < 0.002), and dyslipidemia (74.4% vs. 58.6%, p > 0.002) was higher in patients with carotid plaques than in those without carotid plaques.
Multiple logistic regression analysis showed independent nonmodifiable risk factors for CP like advanced age (age >60 years) and male sex as shown in Table 1.
Comparing the regression analysis in the CP versus non-CP group, the modifiable risk factors, i.e., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia were independent risk factors for CP (Table 1).
The frequency of smoking was also higher in CP patients; however, it did not reach statistical significance, (p-value 0.07) Table 1.
In our study, the majority (56.4%) of CPs were located in the common carotid artery and were predominantly of homogenous consistency (62.1%). This study showed predominantly left carotid artery involvement; however, bilateral involvement of both arteries was also noted (Table 2).
Discussion
This study describes the frequency of carotid plaques in asymptomatic high-risk individuals. In addition, this study explores the various modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors linked with carotid artery disease that predisposes individuals toward a major risk of stroke and myocardial infarction in the local population.
Regarding the patient demographic data; and CP prevalence, no specific differences were identified in loco regional reports. In our study, we excluded known patients with stroke and MI; However, an overall CP prevalence of 42.6% and a significantly higher prevalence in men (57.10%) were noted. In a study by Gul et al. 16 in which they tried to find out sonographic comparison of atherosclerotic changes in carotid arteries of diabetic and nondiabetic individuals, the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography of common carotid artery, and internal carotid artery was reported high for the detection of atherosclerosis changes due to diabetes.16 Colossal studies around the globe from different regions of Asia, Europe, and America in population-based studies showed similar results. Caucasians showed a CP prevalence of 70%, Hispanics showed 52%, and blacks showed 58%.17 Similar trends were reported by Chinese authors18. The rest of the demographics, i.e., mean age and body mass index, and DUS findings such as the location and consistency of plaques, were also comparable.
Various risk factors such as older age, male sex, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and present history of smoking were analyzed in our study. Age is always considered an important risk factor for CP. In the present study, multiple logistic regression analysis showed an independent association of nonmodifiable risk factors with CP, advanced age (age >60 years), and male sex (p-value < 0.0001). The rest of the conventional modifiable risk factors, hypertension, and diabetes have been significantly associated with CP.
In a study by Naseer et al.,19a total of 366 patients underwent bilateral carotid Doppler ultrasound examinations. The results revealed that 156 patients (42.62%) had carotid plaques, with the majority being male (105, or 67.53%). The average age was 61.17 ± 9.54 years, and the average body mass index was 25.43 ± 3.40 kg/m². The left carotid artery exhibited the highest number of plaques (64 or 41.03%), with the common carotid artery being the most frequent location (88 or 56.41%). Most plaques were homogenous (88 or 56.41%). In concordance with the present study, they also reported common comorbidities as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
However, on the basis of the results of the present study, this screening predicts the chances of the development of carotid plaques higher in high-risk patients. However, asymptomatic, as similarly reported by Wang et al. 20 where such patients presented with transient ischemic attacks or permanent neurological damage.
Limitations of the Study
First, the study population was from an urban population in Pakistan, and there was a limited representation of data. Second, the cross-sectional study design may have led to selection bias, especially among healthy elderly individuals. However, patients with previous histories of cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease were excluded from this study. It was beyond the scope of this article to segregate rural and urban populations and further evaluate carotid intima thickness, and carotid stenosis and compare them with risk factors. This study cannot asses the quantitative relationship between CP severity and risk factors.
Conclusion
The findings of this study reveal that that there is a higher frequency of CPs in the middle to old-age population referred for carotid artery scans. Advanced age, male sex, hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia are significant risk factors for CPs.
Acknowledgement
The authors sincerely acknowledge and thank Mr. Waqas Latif, Biostatistician, University of Health Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan, for facilitating us with the statistical analysis of this study.
List of abbreviations
| CA | Carotid arteries |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CPs | Carotid plaques |
| DUS | Duplex Doppler ultrasound |
| CIMT | Carotid intima-media thickness |
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Grant support and financial disclosure
None to disclose.
Ethics approval
The ethical approval of the study was issued by the Institutional Ethical Committee of Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan vide letter No. SZMC/IRB/Internal/MD/100/18, dated 07/11/2019.
Authors’ contributions
MN, MF, ZG: Conception and design of study, acquisition of data, drafting of manuscript, critical intellectual input.
AN, SS, WA:Acquisition of data, interpretation of images, drafting of manuscript, critical intellectual input.
ALL AUTHORS: Approval and responsibility of the final version of the manuscript to be published.
Authors ’ Details
Madiha Naseer1, Mahwish Farzana2, Zeeshan Ghous3, Amna Nasir4, Saulat Sarfraz5, Waqar Ahmed6
- Department of Radiology, Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Federal Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lahore, Pakistan
- Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology Farooq Hospital, Lahore. Pakistan
- Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology, Punjab Institute of Cardiology Lahore, Pakistan
- Medical Officer, Cardiology Department, Shaikh Zayed Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- Professor and Head, Department of Radiology, Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Federal Postgraduate Medical Institute, Lahore, Pakistan
- Consultant Cardiologist, Self-employed. Sargodha, Pakistan.
References
- Björkegren JL, Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis: recent developments. Cell. 2022;185(9):1481–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.004
- Effoe VS, McClendon EE, Rodriguez CJ, Wagenknecht LE, Evans GW, Chang PP, et al. Diabetes status modifies the association between carotid intima-media thickness and incident heart failure: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128(6):58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.04.009
- Yamashita A, Asada Y. Pathology of coronary atherosclerotic plaques and mechanisms of plaque disruption. Ann Nucl Cardiol. 2017;3(1):66–72. https://doi.org/10.17996/anc.17-00011
- Wang Y, Meng R, Liu G, Cao C, Chen F, Jin K, et al. Intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;124(4):118–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.11.008
- Wang C, Lv G, Zang D. Risk factors for carotid plaque and carotid common artery intima-media thickening in a high-stroke-risk population. Brain Behav. 2017;7(11):e00847. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.847
- Song P, Fang Z, Wang H, Cai Y, Rahimi K, Zhu Y, et al. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modeling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(5):e721–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(20)30117-0
- Pelisek J, Wendorff H, Wendorff C, Kuehnl A, Eckstein HH. Age-associated changes in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Ann Med. 2016;48(7):541–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2016.1204468
- Lu J, Ma X, Shen Y, Wu Q, Wang R, Zhang L, et al. Time in range is associated with carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(2):72–8. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2019.0251
- Hoke M, Schillinger M, Minar E, Goliasch G, Binder CJ, Mayer FJ. Carotid ultrasound investigation as a prognostic tool for patients with diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):1–8.
- Castelblanco E, Betriu À, Hernández M, Granado-Casas M, Ortega E, Soldevila B, et al. Ultrasound tissue characterization of carotid plaques differs between patients with type 1 diabetes and subjects without diabetes. J Clin Med. 2019;8(4):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040424
- Katsiki N, Banach M, Mikhailidis DP. Is type 2 diabetes mellitus a coronary heart disease equivalent or not? Do not just enjoy the debate and forget the patient! Arch Med Sci. 2019;15(6):1357–64. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2019.89449
- Ishaque M, de Havenon A, McNally JS, Kalani MY, Park MS. Introduction to management of carotid disease. Carotid Artery Dis. 2020;1(1):1–5.
- Ji X, Leng XY, Dong Y, Ma YH, Xu W, Cao XP, et al. Modifiable risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(22):1–7. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.10.115
- Amor AJ, Catalan M, Pérez A, Herreras Z, Pinyol M, Sala-Vila A, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance lipoprotein abnormalities in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and their association with preclinical carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2016;247(4):161–9.
- Touboul PJ, Hennerici MG, Meairs S, Adams H, Amarenco P, Bornstein N, et al. Mannheim carotid intima-media thickness and plaque consensus (2004–2006–2011): an update on behalf of the advisory board of the 3rd and 4th Watching the Risk Symposium 13th and 15th European Stroke Conferences, Mannheim, Germany, 2004, and Brussels, Belgium, 2006. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;34(4):290–6.
- Gul Z, Tazeen A, Farooq SM, Shabbir I, Asif M, Gilani SA, et al. Sonographic comparison of atherosclerotic changes in carotid arteries of diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. Pak J Med Health Sci. 2022;16(6):779. https://doi.org/10.53350/pjmhs22166779
- Yang D, Iyer S, Gardener H, Della-Morte D, Crisby M, Dong C, et al. Cigarette smoking and carotid plaque echo density in the Northern Manhattan Study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;40(3-4):136–43.
- Zhan C, Shi M, Yang Y, Pang H, Fei S, Bai L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for carotid plaque among middle-aged and elderly adults in rural Tianjin, China. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23870
- Naseer M, Farzana M, Khan MAA, Nasir A, Ahmad A, Javed S, et al. Routine assessment of carotid plaques on Doppler USG and associated presenting symptoms at a tertiary care centre, Lahore. Int J Health Sci. 2023;6(S9):4720–8. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6nS9.13996
- Wang J, An Z, Li B, Yang L, Tu J, Gu H, et al. Increasing stroke incidence and prevalence of risk factors in a low-income Chinese population. Neurology. 2015;84(4):374–81.
