Original Article
Volume: 40 | Issue: 3 | Published: Sep 25, 2024 | Pages: 123 - 129 | DOI: 10.24911/BioMedica/5-1167
Diagnostic accuracy of frozen section in pediatric brain lesions considering histopathology as a gold standard. An experience at a Tertiary Care Center
Authors: Mahvish Hussain , Laeeq ur Rahman , Shazia Riaz , Prof Dr Samina Zaman , Alia Ahmad , Amber Goraya
Article Info
Authors
Mahvish Hussain
Associate Professor, Dept of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Laeeq ur Rahman
Associate Professor, Department of Neurosurgery, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Shazia Riaz
Assistant Professor, Dept of Hematology & Oncology, University of Child Health Sciences & Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Prof Dr Samina Zaman
Professor, Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Alia Ahmad
Professor , Department of Hematology & Oncology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Amber Goraya
Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
Publication History
Received: June 03, 2024
Accepted: September 10, 2024
Published: September 25, 2024
Abstract
Background and Objective: Evaluation of intraoperative frozen section (FS) in central nervous system (CNS) lesions is an invaluable tool to ensure adequacy of tissue obtained to establish the diagnosis and is consistently practiced for rapid assessment and ancillary studies. The objective of this study was to determine the diagnostic concordance between frozen section for the pediatric CNS lesions considering Histopathology as a gold standard in the local pediatric population with respect to age and gender.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted at the Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan. The biopsy specimens from 35 pediatric patients with CNS tumors were sent fresh frozen and in formalin, both, for analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of FS while taking formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues as gold standard.
The data was analyzed by using statistical tests of significance.
Results: Comparing FS with FFPE tissues, 77.1 % cases showed complete concordance, 17% were partially concordant while only 5.7% cases were discordant. Male patients demonstrated higher (10.5%) discordance as compared to females (0%) (p= 0.251). Across age groups, concordance rates vary with no statistically significant differences.
Conclusion: The diagnostic concordance of frozen sections is quite higher in CNS lesions in comparison to formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues with certain limitations occurring in different tumors. Histopathological review and clinical correlation is mandatory for reaching a conclusive diagnosis in challenging cases.
Keywords: frozen section, histopathological diagnosis, concordance
Biomedica - Official Journal of University of Health Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
Volume 40(3):123-129
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Diagnostic accuracy of frozen section in pediatric brain lesions considering histopathology as a gold standard. An experience at a Tertiary Care Center
Mahvish Hussain1*, Laeeq ur Rahman2, Shazia Riaz3, Samina Zaman4, Alia Ahmad5, Amber Goraya6
Received: 03 June 2024 Revised date: 11 July 2024 Accepted: 10 September 2024
Correspondence to: Dr. Mahvish Hussain
*Associate Professor, Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences & the Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan.
Email: mahvish66@gmail.com
Full list of author information is available at the end of the article.
ABSTRACT
Background and Objective:
Evaluation of intraoperative frozen section (FS) in central nervous system (CNS) lesions is an invaluable tool to ensure the adequacy of tissue obtained to establish the diagnosis and is consistently practiced for rapid assessment and ancillary studies. The objective of this study was to determine the diagnostic concordance between FS for the pediatric CNS lesions considering histopathology as a gold standard in the local pediatric population with respect to age and gender.
Methods:
This cross sectional study was conducted at the Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences and the Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan. The biopsy specimens from 35 pediatric patients with CNS tumors were sent fresh frozen and in formalin, both, for analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of FS while taking formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues as the gold standard.
The data were analyzed by using statistical tests of significance.
Results:
Comparing FS with FFPE tissues, 77.1% of cases showed complete concordance, 17% were partially concordant while only 5.7% of cases were discordant. Male patients demonstrated higher (10.5%) discordance as compared to females (0%) (p = 0.251). Across age groups, concordance rates vary with no statistically significant differences.
Conclusion:
The diagnostic concordance of FSs is quite higher in CNS lesions in comparison to FFPE tissues with certain limitations occurring in different tumors. Histopathological review and clinical correlation is mandatory for reaching a conclusive diagnosis in challenging cases.
Keywords:
Pediatric brain lesions, frozen section, histopathological diagnosis, concordance, discordant, formalin, cryostat, neurosurgery.
Introduction
Pediatric brain tumors are the most common solid malignancies of childhood 1-3 and are considered as the second most common malignant tumors after leukemias.1 Intracranial space occupying lesions imposes significant mortality and morbidity. They can be of infective and non-infective etiology. In developing countries, infective space-occupying lesions play a significant role.4 Pediatric brain tumors account for about 20% of all malignant tumors in the pediatric population under 15 years of age.1,3 To pographical variations in incidence rates have been noted with the Western population reporting a higher incidence (30 per million person-years) as compared to Africa (10 per million years) and Asia (15 per million years). As per available data of World Health Organization (WHO) from Pakistan, the rate of the central nervous system (CNS) tumors was 0.89/100,000 in the pediatric population.5 However, in low-income countries, the prevalence of pediatric brain tumors varies from 6.1% to 49.6%.6
The current WHO classification describes more than 130 different CNS tumors, entities, or variants.7 Classically, these tumors are diagnosed by histopathological analyses of surgically removed tissue followed by immunohistochemistry along with magnetic resonance imaging.8 The WHO classification of CNS neoplasms underwent a paradigm shift in 2016 with the incorporation of molecular data with the morphological features, such that several new entities came to be distinctly defined.9
Over time, it is likely that the detection and monitoring of molecular alterations will be critical for the clinical management of these tumors.8
Evaluation of intraoperative squash smear or frozen section (FS) in CNS neoplasms is consistently practiced at many centers for rapid assessment and has several advantages to its credence. It is an invaluable tool to ensure the adequacy of tissue obtained to establish the diagnosis. Moreover, it aids in guiding the surgeon in critical decisions regarding the extent of resection. Although molecular markers have been integrated with morphology in the revised 2016 WHO classification of brain tumors, precise morphological assessment still remains the foundation for the diagnosis, and rapid intraoperative assessment of morphological details is equally critical and rewarding.7
Intraoperative consultation for intracranial lesions is widely used to assist neurosurgical treatment decisions. From a neurosurgical viewpoint, intraoperative consultation on neurosurgical specimens is a valuable guide for the best intra or postoperative patient management. FS of a suspected CNS neoplasm is chiefly performed to assess the adequacy of the submitted tissue in the setting of stereotactic biopsies, and several ancillary studies can be performed on the submitted tissue before routine processing.10,11 In addition, tumors such as astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas can be intraoperatively diagnosed with great success using smear cytology, and the diagnostic yield for most tumor types can be substantially increased when crush smears and FSs are used simultaneously. The accuracy of FS diagnosis of CNS lesions has been debated worldwide, and multiple factors should be considered to make accurate diagnoses.10
Brain tumors represent a significant group of tumors seen in the pediatric population. Since the prevalence, frequency, and location of the different histologic types of brain tumors vary significantly between children and adults, it is reasonable to expect that diagnoses entertained during intraoperative consultation will also differ, influencing the aggressiveness of surgical resection and course of management. It is, therefore, imperative for surgical pathologists responsible for pediatric patients to become familiar with these entities and the diagnostic challenges they pose during the course of surgery.12-15
The objective of this study was to determine the diagnostic concordance between FS keeping histopathological examination on formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues as a gold standard in different brain lesions presenting in the local pediatric patients and analyzing them with respect to gender, age, and type of tumors.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted at the Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences and The Children’s Hospital, (UCH&CH) Lahore, a major neurosurgical referral center, over a period of 15 months since Jan 2022 till March 2023 to evaluate the diagnostic concordance between FS and formalin-fixed tissues with regards to histopathological examination in pediatric brain lesions.
A sample size of 35 was calculated through WHO calculator.16 Children of the age range of 3 months till 16 years of both genders, with CNS lesions presenting for the primary diagnosis, were included. Necrotic tissue or if the samples were sent in saline or unfit for histopathological diagnosis or the patients with recurrence of tumors or already availed surgical or medical therapy, were excluded.
Thirty five pediatric patients underwent surgical resection of CNS lesions by expert neurosurgeons. FS was prepared from fresh tissue, and processed by rapidly cooling the tissue through a cryostat in the Histopathology Department which converts tissue water into ice and makes the tissue rigid for cutting into slices followed by staining with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The FS slides were examined by two consultant histopathologists and reported within 20 minutes of receiving the samples in the laboratory. Other biopsy fragments were collected in formalin and permanent paraffin-embedded sections were prepared, stained with H&E, and diagnosed based on morphological features and immunohistochemical stains. Patient demographics, clinical data, and radiological findings were collected from the available medical records.
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of (UCHS&CH) Lahore, Pakistan and written informed consent was taken from the parents of all the patients.
The comparison between FS and FFPE tissues was reported as concordance with complete concordance labeled when the intraoperative final diagnosis based on FS was the same as the final histopathological diagnosis on FFPE tissues. Few cases were labeled as partially concordant when the diagnosis of FS was not wrong completely but too broad to characterize it as fully concordant. Discordant cases were labeled as the ones whose FS diagnosis was completely different from the FFPE histopathological diagnosis.7
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using Statistical Package of Social Sciences version 26. The frequency of diagnostic categories in FS and FFPE diagnosis was compared using chi-square tests. ANOVA was used to compare the means of continuous variables. The diagnostic disparity between FS and histopathological examination was evaluated by comparing the frequency of diagnostic categories. Histopathological examination was considered the gold standard.
Results
The age distribution of the 35 patients under study shows a varied range, with 2 patients (5.71%) under 1 year, 8 patients (22.86%) between 1 and 3 years, 12 patients (34.29%) between 4 and 7 years, 10 patients (28.57%) between 8 and 10 years, 2 patients (5.71%) between 11 and 13 years, and 1 patient (2.86%) under 14 years. This distribution indicates that the majority of patients (34.29%) fall in the 4-7 years age range, followed closely by the 8-10 years range (28.57%), with the remaining patients spread across the other age categories, adding up to a total of 35 patients (100%).
A slight male preponderance (19, 54.2%) was observed with male to female ratio of 1.18
In the present study, females showed 75% concordance, 25% partial concordance, and 0% discordance, while males demonstrated 78.9% concordance, 10.5% partial concordance, and 10.5% discordance, with a non-significant p-value of 0.251 (Table 1). Across age groups, concordance rates vary, with the highest rate (100%) in the 8-10 years’ group and the lowest rate (50%) in the <1 year and 11-13 years groups (Table 2). Overall, the results suggest a high level of concordance, with some variation across demographic groups, but no statistically significant differences were observed.
The concordant group (n = 27) has a mean age of 5.60 years (SD = 2.91), ranging from 0.75 to 11.30 years, with a non-significant p-value of 0.494. The partially concordant group (n = 6) has a higher mean age of 7.29 years (SD = 5.27), ranging from 0.92 to 15.00 years. The discordant group (n = 2) has a mean age of 4.75 years (SD = 2.47), ranging from 3.00 to 6.50 years. Overall, the total sample (n = 35) has a mean age of 5.84 years (SD = 3.35), ranging from 0.75 to 15.00 years.
Amongst the cases under study, most of them were neoplastic (32, 91.4%) and out of neoplasms, pilocytic astrocytoma (PA) was the most frequent tumor (13.40%).
Out of a total of 35 cases, there were 27 (77.1%) cases were found to have the same diagnosis on FS as well as FFPE sections. They were labeled as completely concordant (Figures 1 and 2). There were 6 (17.1%) cases that were labeled as partially concordant as 2 of these 6 were rendered the diagnosis under the umbrella of glioma but could not be subtyped as PA WHO Grade 1. One case diagnosed as pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) WHO grade 2 on FFPE but labelled as glioma on FS (Figure 3). There were 2 cases diagnosed on FFPE as Ependymoma (EPN) which were also labeled as gliomas on FS as their subtyping was not possible due to poor morphology. There was 1 case of dermoid cyst which was given the descriptive diagnosis on FS, and finally, it proved to be as dermoid cyst on FFPE also. In the present study, there were only 2 (5.71%) cases that differed on FS from FFPE sections absolutely and they were labeled as completely discordant. One of them was Ewings sarcoma which showed high cellularity and pleomorphism and was labelled as high grade glioma (HGG) on FS. Another one was Medulloblastoma (MB) WHO grade 4, which was also a highly cellular tumor with neoplastic cells arranged in sheets diagnosed on FS as HGG but ultimately turned out to be MB (Figure 4).
Table 1. Diagnostic concordance rates by demographic characteristics of patients under study.
| Concordant n (%) |
Partial concordant n (%) |
Dis-concordant n (%) |
p-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 12 (75) | 4 (25) | 0 | 0.251 |
| Male | 15 (78.9) | 2 (10.5) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| Age (Years) | <1 years | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | 0.182 |
| 1-3 years | 7 (87.5) | - | 1 (12.5) | ||
| 4-7 years | 8 (66.7) | 3 (25) | 1 (8.3) | ||
| 8-10 years | 10 (100) | 0 | 0 | ||
| 11-13 years | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | 0 | ||
| <14 years | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
Table 2. Age of the patients by concordance status.
| Age of the patient (Year) | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concordant | 27 | 5.60 | 2.91 | 0.75 | 11.30 | 0.494 |
| Partial concordant | 6 | 7.29 | 5.27 | 0.92 | 15.00 | |
| Dis-concordant | 2 | 4.75 | 2.47 | 3.00 | 6.50 | |
| Total | 35 | 5.84 | 3.35 | 0.75 | 15.00 |
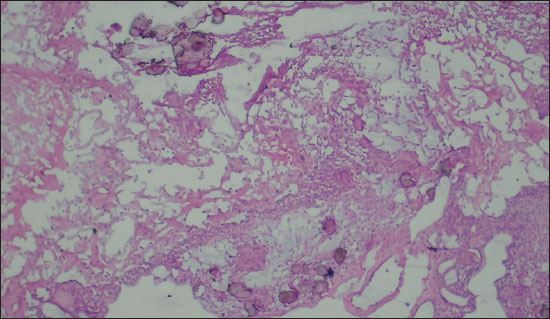
Figure 1. Photomicrograph showing foci of calcification along with epithelial cells on FS (Diagnosed as Craniopharyngioma on FS; 200X, H&E).
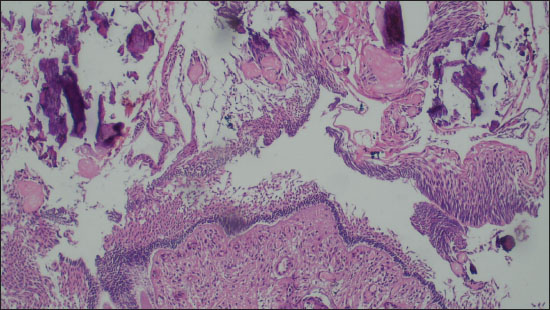
Figure 2. Photomicrograph comprising of ghost cells, proliferating basaloid cells and foci of calcification (Diagnosed as Craniopharyngioma on FFPE; 200X, H&E).
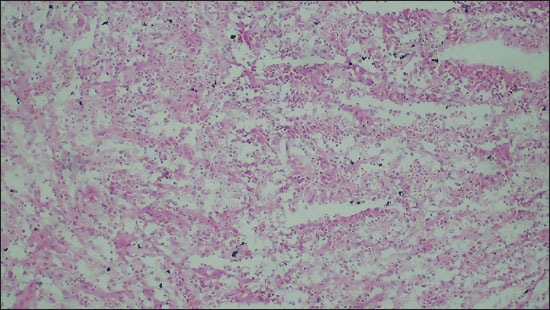
Figure 3. Photomicrograph showing a neoplasm with increased cellularity arranged in sheets on FS (Diagnosed as Glioma on FS; 100X, H&E).
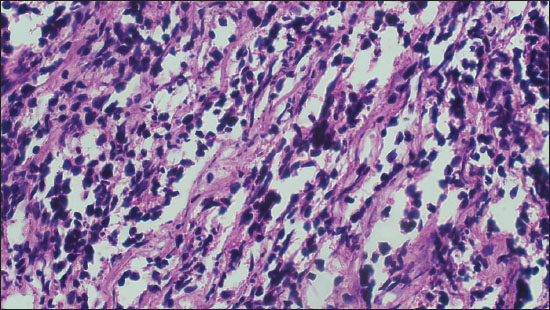
Figure 4. Photomicrograph comprising of neoplastic with hyperchromatic nuclei arranged in sheets on FFPE sections (Diagnosed as MB on FFPE; 200X, H&E).
Discussion
The present study is based on the diagnosis of CNS lesions in the pediatric population in a tertiary healthcare center with a special emphasis on the utility of FS diagnosis in comparison to FFPE diagnosis. In our local setup, this is the first study being carried out in the pediatric population. In the present study, a total of 35 lesions of CNS being diagnosed on FS, were correlated with the final histopathological diagnosis on FFPE sections. The present study was based on pediatric patients only as being done in one of the largest pediatric tertiary care centers in Asia, in contrast to Khan et al.17 whose study population was adults only with the mean age of the patients as 36.7 + 8.76 years. However, similar to our findings Khan et al.17 also observed a male preponderance. The majority of the lesions in our study were neoplastic (91.4%), similar to Yadav et al.7 who also observed the majority of the lesions (95.6%) as neoplastic in their study.
In the present study, there was a strong concordance between the diagnosis made on FS and FFPE sections (Figures 3 and 4). We concluded diagnostic concordance in our study as 77.1% while only two cases were absolutely discordant with each other (5.7%). One was a case of Ewing sarcoma which was diagnosed as a high-grade glial neoplasm on FS. This interpretation was due to poor morphological details of FS. The second case was of MB which was diagnosed as a high-grade glioma on FS. Khan et al.17 also showed a sensitivity of FS to be 83% in their study and another study from Pakistan, where Ud Din et al.18 reported diagnostic accuracy of FS as 90%. Similar to our findings where we observed 77.1% complete concordance, 17.1% cases had partial concordance and only 5.7% were completely discordant, Yadav et al.7 also observed 70% complete concordance, 20.1% partial concordance, and 9.9% complete disconcordance.
Similar to our study, Rao et al.19 observed that 6% of cases were found to be discordant. These included angiomatous meningioma, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, metastatic renal cell carcinoma, cerebellopontine angle fibrous meningioma, and craniopharyngioma. In 29 cases, a definite opinion could not be given on FS as the samples examined were nondiagnostic and included only necrotic, calcified, fibrous, or glial tissue. This is due to heterogeneity of CNS neoplasms and sampling error. Twelve cases were given as glial tissue, and the permanent section revealed 10 cases to be low-grade glioma and two cases to be hypothalamic hamartoma. The two cases diagnosed as fibrous tissue turned out to be meningioma. One of the common difficulties involves a diagnosis of spindle cell neoplasm in FS.19 On contrary to our study, Plesec and Prayson 20 reported a discrepancy in 13% of the cases involving spindle cell lesions, most commonly confusing schwannomas, and meningiomas with other lesions.
Interpretation of FS is mostly a challenge for histopathologists. Certain factors including the fragile nature of the intra cranial lesions, extreme vascularity, and high water content of the brain tissue along with freezing artifacts and inadequacy of the specimen lead to interpretation difficult.7,17 CNS tumors are a major health concern because of increasing frequency, high morbidity, high mortality, and poor prognosis. These neoplasms comprise 2% of all cancers and in children the second most common type of cancer.12,13,15
There were six cases (17.1%) in our study which showed partial concordance. Five of them were diagnosed under the umbrella of glioma. Out of those five cases, 2 were diagnosed on FFPE sections as PA, two were finally diagnosed as EPN and one case was of PXA. One case was given a descriptive diagnosis and it was finally rendered as a dermoid cyst.
Regragui et al.21 had a study population of 1,315 patients and found most discrepancies in gliomas, hemangioblastomas, and metastatic tumors. However, their concordance rate was 87.6%.
Discrepancies between the FS and the permanent diagnoses were reported in many studies. Some studies showed discrepancies in EPN, glioblastoma, metastatic tumors, oligodendroglioma, meningioma, and astrocytoma.22,23 Savargaonkar and Farmer 23 observed the discrepancy in spindle cell lesions, astrocytoma versus oligodendroglioma, lymphoma, reactive versus neoplastic process, and tumor overgrading. However, they observed the diagnostic concordance in 94% of cases.23
Discrepant cases need to be reviewed by histopathologists to familiarize themselves with the morphological changes and artifacts. The knowledge of possible errors could minimize misinterpretation and help to provide a more conclusive opinion to the operating surgeon.24
Limitations of the Study
The present study is based on only 35 cases which is quite a small number based on the availability of FS in this group of patients. The reason behind it being in the public sector we face the difficulty of technical shortcomings like shortage of trained man power and nonavailability of cryostat-related chemicals which make histopathological diagnosis onFFPE as more convenient and frequent method of diagnosis.
Conclusion
The diagnostic concordance of FSs is quite higher in CNS lesions as compared to FFPE tissues. Gross inspection, sampling by a trained neurosurgeon, and diagnosis on FSs complemented with cytological, histological, and radiological correlation can avoid certain limitations and provide a rapid, reliable, and cost-effective diagnostic modality necessary for optimum patient care.
Acknowledgement
The authors sincerely acknowledge and thank the help rendered by Mr. Munawar Ghous, Statistician, University of Child Health Sciences and The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan, for facilitating us with the statistical analysis of this study.
List of Abbreviations
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| EPN | Ependymoma |
| FFPE | Formalin fixed paraffin embedded |
| FS | Frozen section |
| HGG | High grade glioma |
| MB | Medulloblastoma |
| PA | Pilocytic astrocytoma |
| PXA | Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| UCHS & CH | The Children’s Hospital University of Child Health Science |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Grant support and financial disclosure
None to disclose.
Ethical approval
The ethical approval of the study was taken from the Institutional Review Board of University of Child Health Sciences and The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan, vide Letter No. 839/CH-UCHS dated:20-05-2023.
Authors’ contributions
MH, SZ, SR: Conception and design of study, acquisition, and interpretation of histopathological data, critical intellectual input, analysis of data, drafting of the manuscript.
AA: Acquisition of data, interpretation of histopathological slides, drafting of manuscript.
AG, LR: Acquisition of data, critical intellectual input, interpretation and analysis of clinical and radiological data, drafting of manuscript.
ALL AUTHORS: Approval and responsibility of the final version of the manuscript to be published.
Authors’ Details
Mahvish Hussain1, Laeeq ur Rahman2, Shazia Riaz3, Samina Zaman4, Alia Ahmad5, Amber Goraya6
- Associate Professor, Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- Associate Professor, Department of Neurosurgery, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- Assistant Professor, Department of Hematology & Oncology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- Professor, Department of Histopathology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- Professor , Department of Hematology & Oncology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, University of Child Health Sciences & The Children’s Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
References
- Simone V, Rizzo D, Cocciolo A, Caroleo AM, Carai A, Mastronuzzi A, et al. Infantile brain tumors: a review of literature and future perspectives. Diagnostics. 2021;11(4):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11040670
- Segal D, Karajannis MA. Pediatric brain tumors: an update. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2016 Jul;46(7):242–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cppeds.2016.04.004
- 3. Fahmideh MA, Scheurer ME. Pediatric brain tumors: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, and future directions. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021;30(5):813–21. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1443
- Pathak S, Batni G. Across sectional study of prevalance, clinical profile and CT scan features of intracranial space occupying lesions. IP Indian J Neurosci. 2020;6(1):46–50. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijn.2020.009
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. WHO IfRoC. Cancer Today; 2020. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/
- Mushtaq N, Resham S, Shamim S, Qureshi BM, Riaz Q, Bouffet E. Childhood medulloblastoma. J Pak Med Assoc. 2020;70(11):2007–16. https://doi.org/10.5455/JPMA.293142
- Yadav M, Sharma P, Singh V, Tewari R, Mishra PS, Roy K. An audit of diagnostic disparity between intraoperative frozen section diagnosis and final histopathological diagnosis of central nervous system lesions at a Tertiary Care Center. J Lab Physicians. 2022;14(4):384–93. https://doi.org/ 10.1055/s-0042-1750064. ISSN 0974-2727.
- Bonner ER, Bornhorst M, Packer RJ, Nazarian J. Liquid biopsy for pediatric central nervous system tumors. Precis Oncol. 2018;2:29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-018-0072-z
- Gupta K, Kapatia G, Salunke P, Ahuja CK, Singh V. Intraoperative consultation in the diagnosis of posterior fossa brain tumors following the 2016 WHO update. Cytopathology. 2021;32(4):459–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/cyt.12966
- Obeidat FN, Awad HA, Mansour AT, Hajeer MH, Al-Jalabi MA, Abudalu LE. Accuracy of frozen-section diagnosis of brain tumors: an 11-year experience from a Tertiary Care Center. Turk Neurosurg. 2019;29(2):242–6. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.23220-18.2
- Çakir E, Oran G, Yüksek GE, Ding C, Tihan T. Intraoperative consultations of central nervous system tumors: a review for practicing pathologists and testing of an algorithmic approach. Turk Patoloji Dergisi. 2019;35(3):173–84. https://doi.org/10.5146/tjpath.2018.01460
- Adesina AM. Frozen section diagnosis of pediatric brain tumors. Surg Pathol Clin. 2010;3(3):769–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.path.2010.07.001
- Nassif M, Brewer J, Gill A. Correlation between brain tumour frozen sections and final diagnoses at Royal North Shore Hospital. Pathology. 2011;43(1):S92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3025(16)33298-6
- Kurdi M, Baeesa S, Maghrabi Y, Bardeesi A, Saeedi R, Al-Sinani T, et al. Diagnostic discrepancies between intraoperative frozen section and permanent histopathological diagnosis of brain tumors. Turk Patoloji Ddergisi. 2022;38(1):34–9. https://doi.org/10.5146/tjpath.2021.01551
- Tofte K, Berger C, Torp SH, Solheim O. The diagnostic properties of frozen sections in suspected intracranial tumors: a study of 578 consecutive cases. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5:170. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.146153
- Uakarn C, Chaokromthong K, Sintao N. Sample size estimation using Yamane and Cochran and Krejcie and Morgan and Green Formulas and Cohen Statistical Power Analysis by G*Power and Comparisons. Apheit Int J. 2021;10(2):76–88.
- Khan SA, Ujjan Badar Uddin, Akhunzada NZ, Anis SB. Diagnostic accuracy of frozen section in detecting malignant brain tumors taking histopathology as gold standard. Professional Med J. 2020;27(9):1814–7. https://doi.org/10.29309/TPMJ/2020.27.09.3835
- Ud Din N, Memon A, Idress R, Ahmad Z, Hasan S. Central nervous system lesions: correlation of intraoperative and final diagnoses, six year experience at a referral center in a developing country, Pakistan. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(6):1435–7.
- Rao S, Rajkumar A, Ehtesham MD, Duvuru P. Challenges in neurosurgical intraoperative consultation. Neurol India. 2009 Jul 1;57(4):464–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.55598
- Plesec TP, Prayson RA. Frozen section discrepancy in the evaluation of nonneoplastic central nervous system samples. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2009;13(6):359–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2009.05.006
- Regragui A, Amarti Riffi A, Maher M, El Khamlichi A, Saidi A. Place de l’examen extemporané dans les tumeurs du système nerveux central. A propos de 1315 observations [Accuracy of intraoperative diagnosis in central nervous system tumors: report of 1315 cases]. Neurochirurgie. 2003;49(2-3 Pt 1):67–72.
- Kini JR, Jeyraj V, Jayaprakash CS, Indira S, Naik CN. Intraoperative consultation and smear cytology in the diagnosis of brain tumours. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2008;6(24):453–7. https://doi.org/10.3126/kumj.v6i4.1734
- Savargaonkar P, Farmer PM. Utility of intra-operative consultations for the diagnosis of central nervous system lesions. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2001;31(2):133–9.
- Al-Ajmi R, Al-Kindi H, George M, Thomas K. Correlation of intraoperative frozen section report and histopathological diagnosis of central nervous system tumors - a six-year retrospective study. Oman Med J. 2016;31(6):414–20. https://doi.org/10.5001/omj.2016.84
